Understanding the Difference Between Tendonitis and Tendinosis
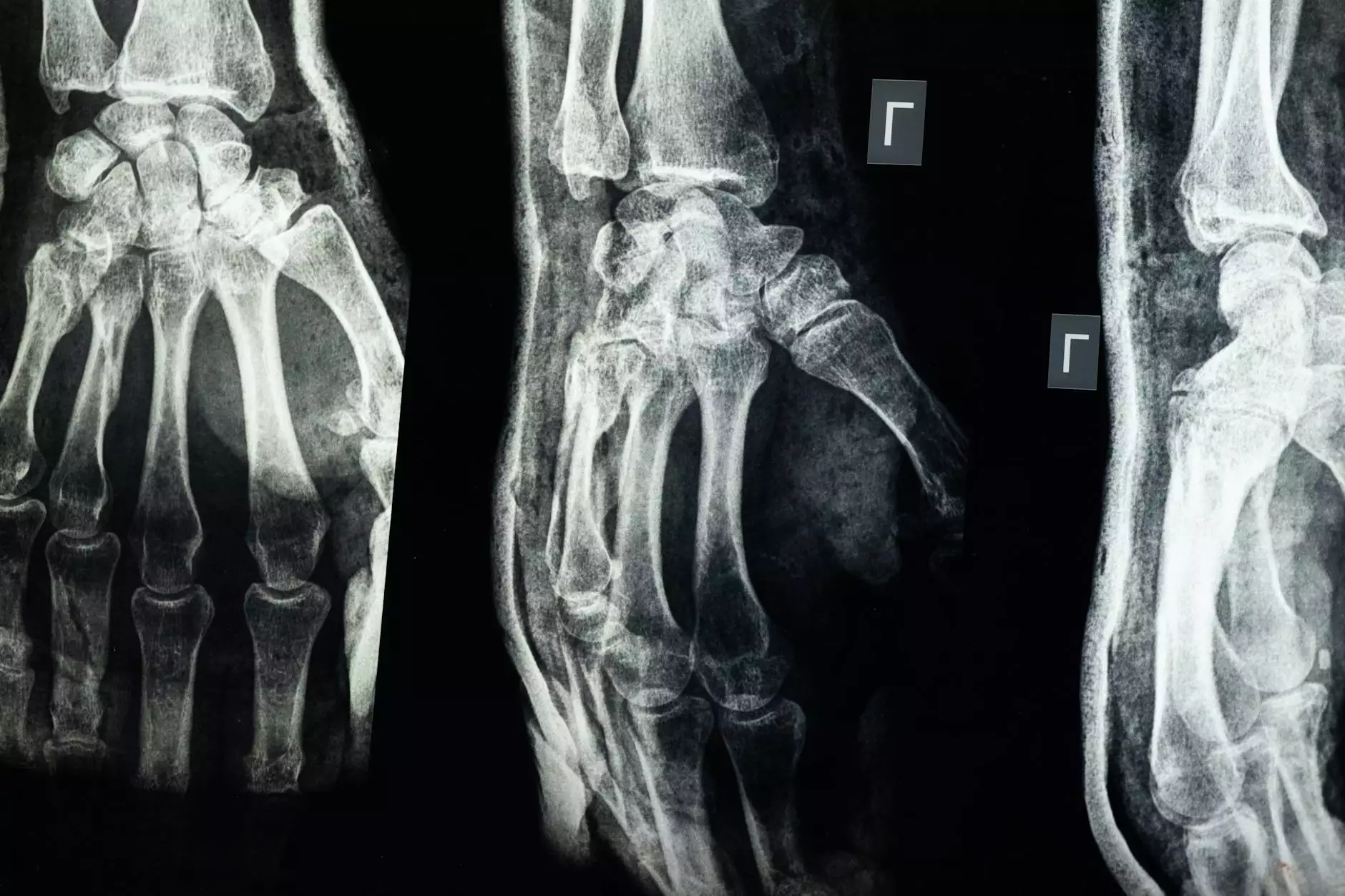
In the realm of Health & Medical, Chiropractors, and Physical Therapy, a common question that often arises is "what is the difference between tendonitis and tendinosis?" These two conditions, although they affect tendons, have distinct characteristics and treatments that are important to differentiate for accurate diagnosis and effective care.
The Basics of Tendonitis
Tendonitis refers to the acute inflammation of a tendon due to overuse or injury. It typically presents with symptoms such as pain, swelling, and tenderness around the affected tendon. The condition is often associated with repetitive movements or sudden increase in physical activity.
Individuals with tendonitis may experience discomfort that worsens with movement and improves with rest. Common sites where tendonitis occurs include the shoulders, elbows, wrists, knees, and ankles.
Understanding Tendinosis
Tendinosis, on the other hand, is a chronic condition characterized by degeneration of the tendon without significant inflammation. Unlike tendonitis, tendinosis is usually caused by repetitive microtrauma to the tendon over time.
People with tendinosis may have pain and stiffness in the affected area, with symptoms becoming more pronounced during activity. Tendinosis is often a result of untreated or recurrent tendonitis that has led to structural changes in the tendon.
Distinguishing Between the Two
One key difference between tendonitis and tendinosis lies in the underlying pathology. While tendonitis involves active inflammation, tendinosis is characterized by chronic degenerative changes in the tendon tissue.
Diagnosing tendonitis may involve imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI to assess inflammation, whereas tendinosis is typically identified based on the structural integrity of the tendon through imaging and physical examination.
Treatment Approaches
Management strategies for tendonitis often focus on reducing inflammation through rest, ice, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications. In contrast, tendinosis treatment aims to promote tendon healing and regeneration through exercises, stretching, and sometimes advanced therapies like shockwave therapy or PRP injections.
Both conditions may benefit from professional guidance from healthcare providers specializing in Chiropractic and Physical Therapy, who can tailor treatment plans to address the specific needs of each individual.
Conclusion
By understanding the disparities between tendonitis and tendinosis, individuals can seek appropriate care and interventions to alleviate pain, improve function, and support tendon health. Whether experiencing acute inflammation or chronic degeneration, timely and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management and recovery.